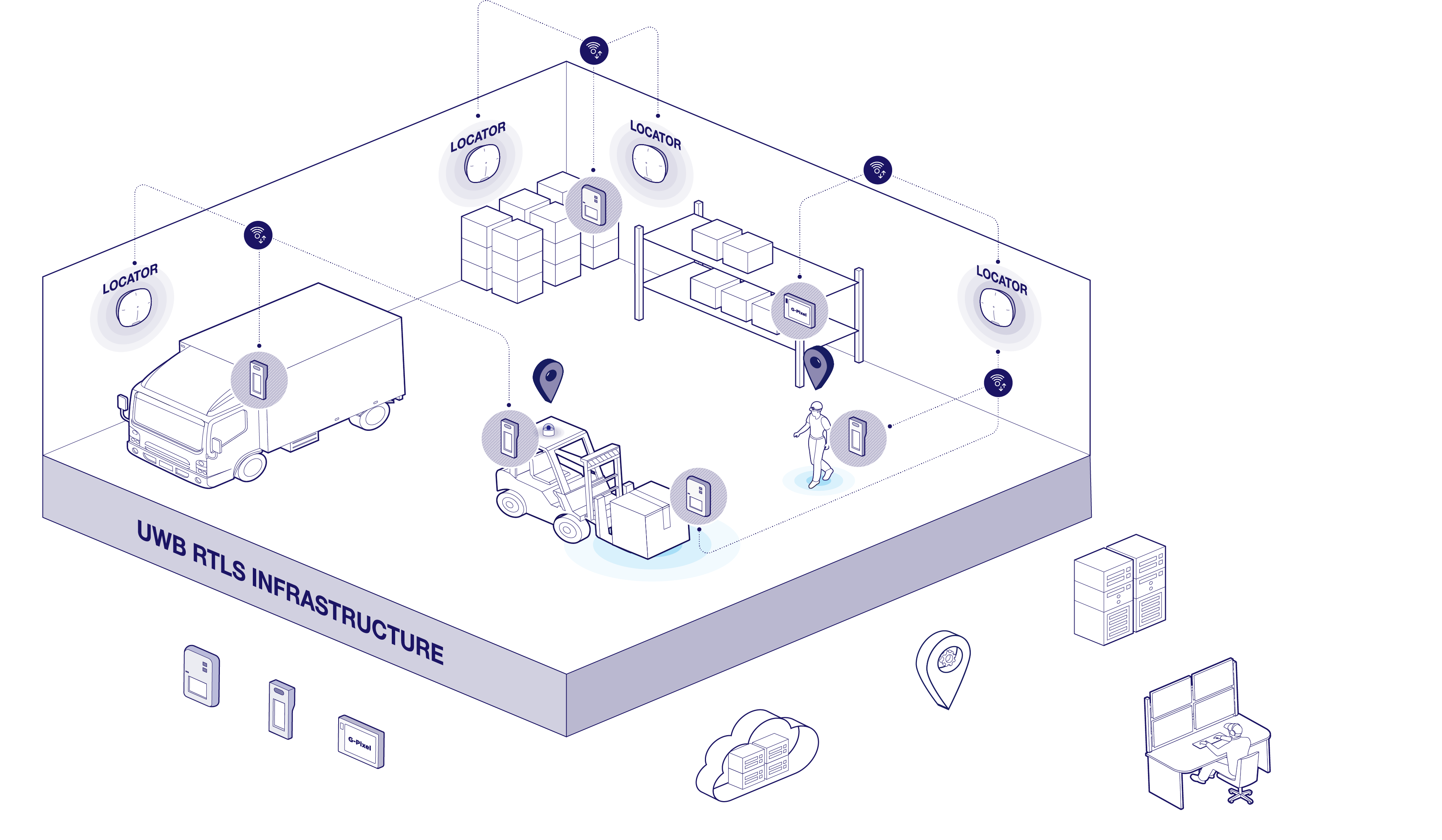
Real Time Location System consists of three components :
RTLS hardware, software and infrastructure. Depending on the project, a tag is carried or attached to detect the movement of people and assets in a space that requires positioning, and “locators” are placed at key points in the space to transmit and receive signals from the tag to calculate and visualize position coordinates through software.
Geoplan is an ultra-wideband communication-based precision indoor positioning technology that provides centimeter-level positioning accuracy.
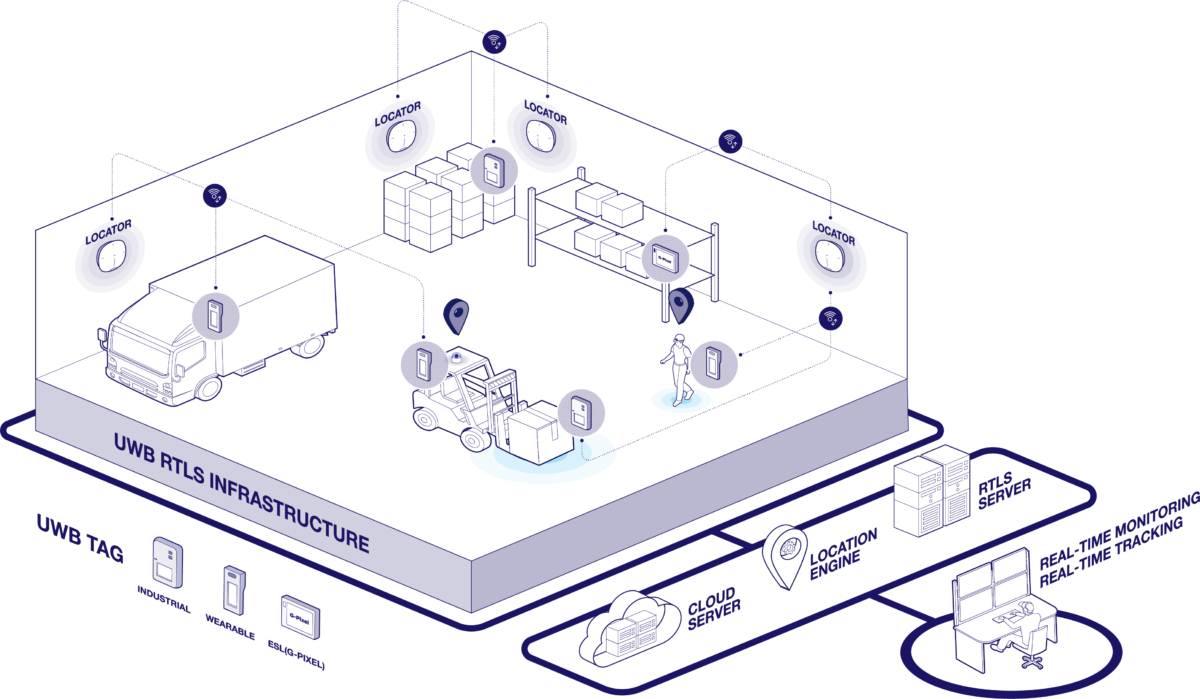
Geoplan is a company specializing in UWB(Ultra-WideBand) communication-based RTLS, providing total solutions including hardware, software and user applications with the highest level positioning technology.
Geoplan accumulated experiences and technologies to expand and operate even on large-scale projects without space limitations, multi-floors and hundreds of tracking targets.
Geoplan provides open API for easy integration with third-party systems, and provides development starter kits and technical training for partners.
Geoplan dedicates itself to satisfy customers with position accuracy with error range of 50 cm through UWB(Ultra-WideBand) communication technology and various position algorithms.
There are various methods for indoor positioning algorithms.
Each method has its pros and cons, and the most commonly used algorithms are as follows:
It calculates the distance between devices through UWB communication between two devices. Compared to the TDoA method, the infrastructure configuration is relatively simple, but the number of devices that can be calculated simultaneously is limited, and battery consumption is higher than TDoA.
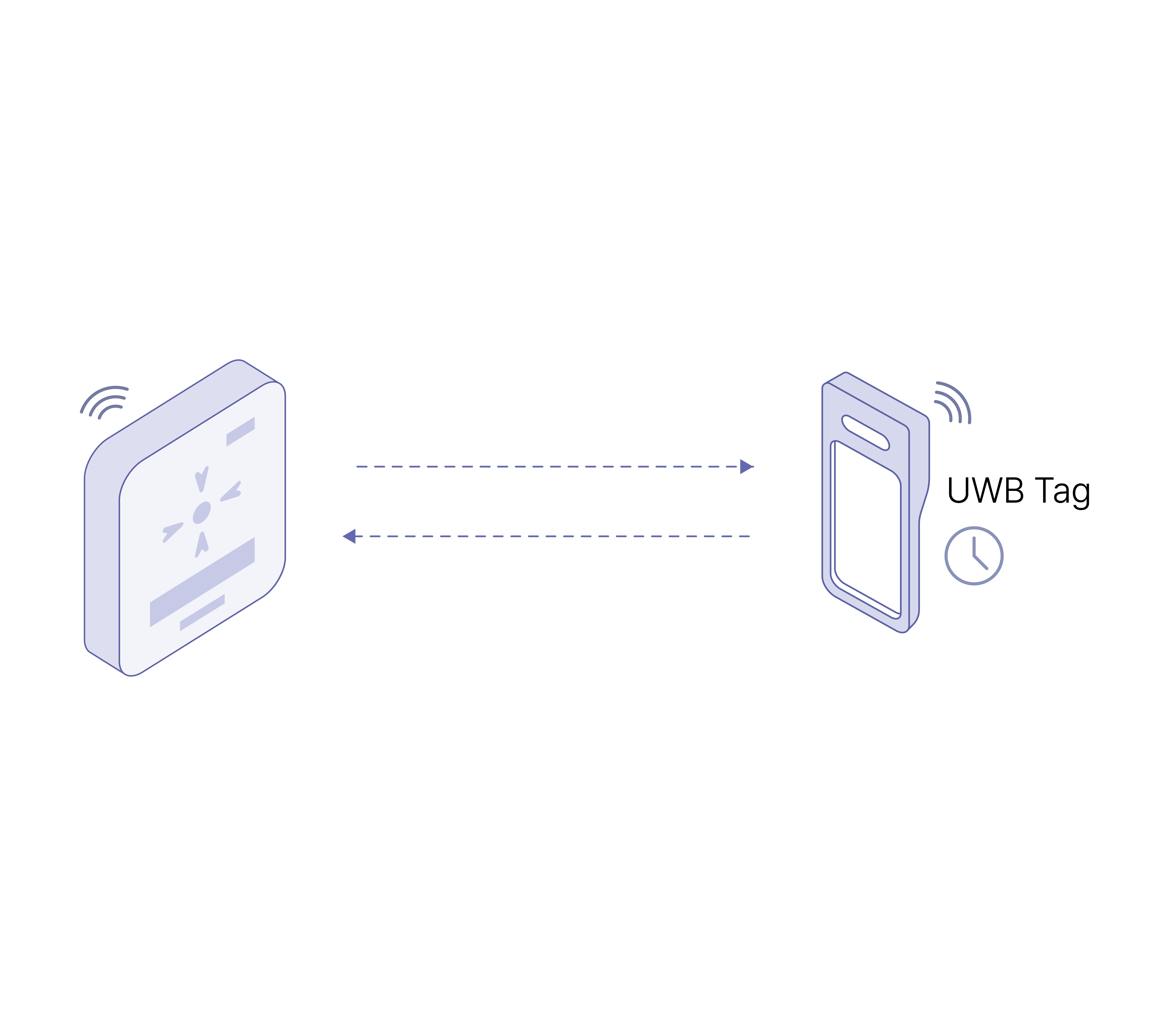
It calculates the distance between devices through UWB communication between two devices. Compared to the TDoA method, the infrastructure configuration is relatively simple, but the number of devices that can be calculated simultaneously is limited, and battery consumption is higher than TDoA.
UWB locator must be precisely synchronized based on the UWB signal, and the position of the device is calculated using the time difference between when the signal sent by the UWB device reaches each locator, and the locator must be synchronized through the UWB signal. Compared TWR, more tags can be positioned quickly and simultaneously, and battery consumption can be minimized.
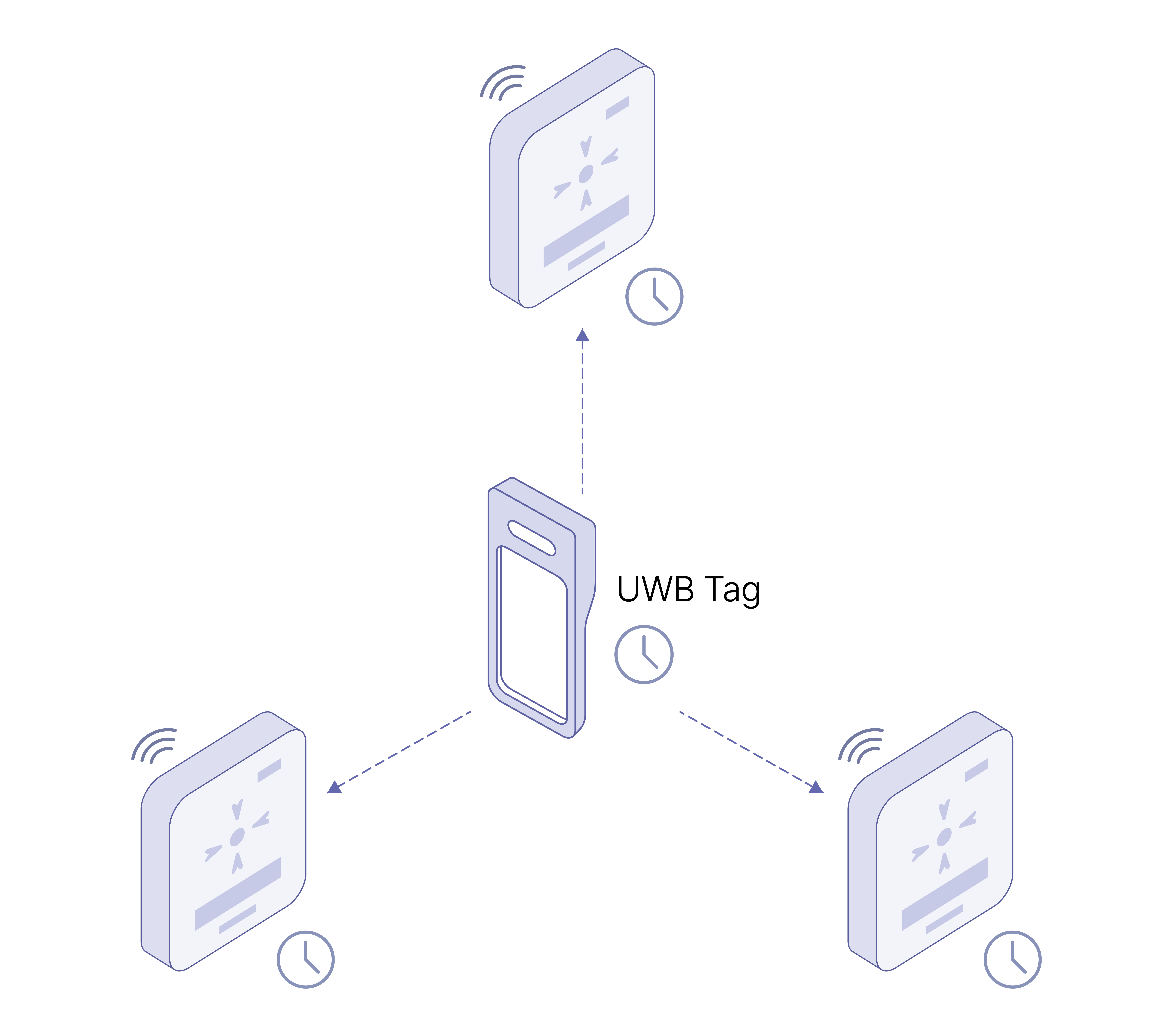
UWB locator must be precisely synchronized based on the UWB signal, and the position of the device is calculated using the time difference between when the signal sent by the UWB device reaches each locator, and the locator must be synchronized through the UWB signal. Compared TWR, more tags can be positioned quickly and simultaneously, and battery consumption can be minimized.
AoA positioning calculates the angle of UWB signals arriving by using the time difference (Phase Difference) arriving at each antenna based on the UWB array antenna in a device, and by substituting the vector value with the position and angle of the locator, the position of the UWB device is identified. Compared to TDoA, positioning can be calculated using less infrastructure.
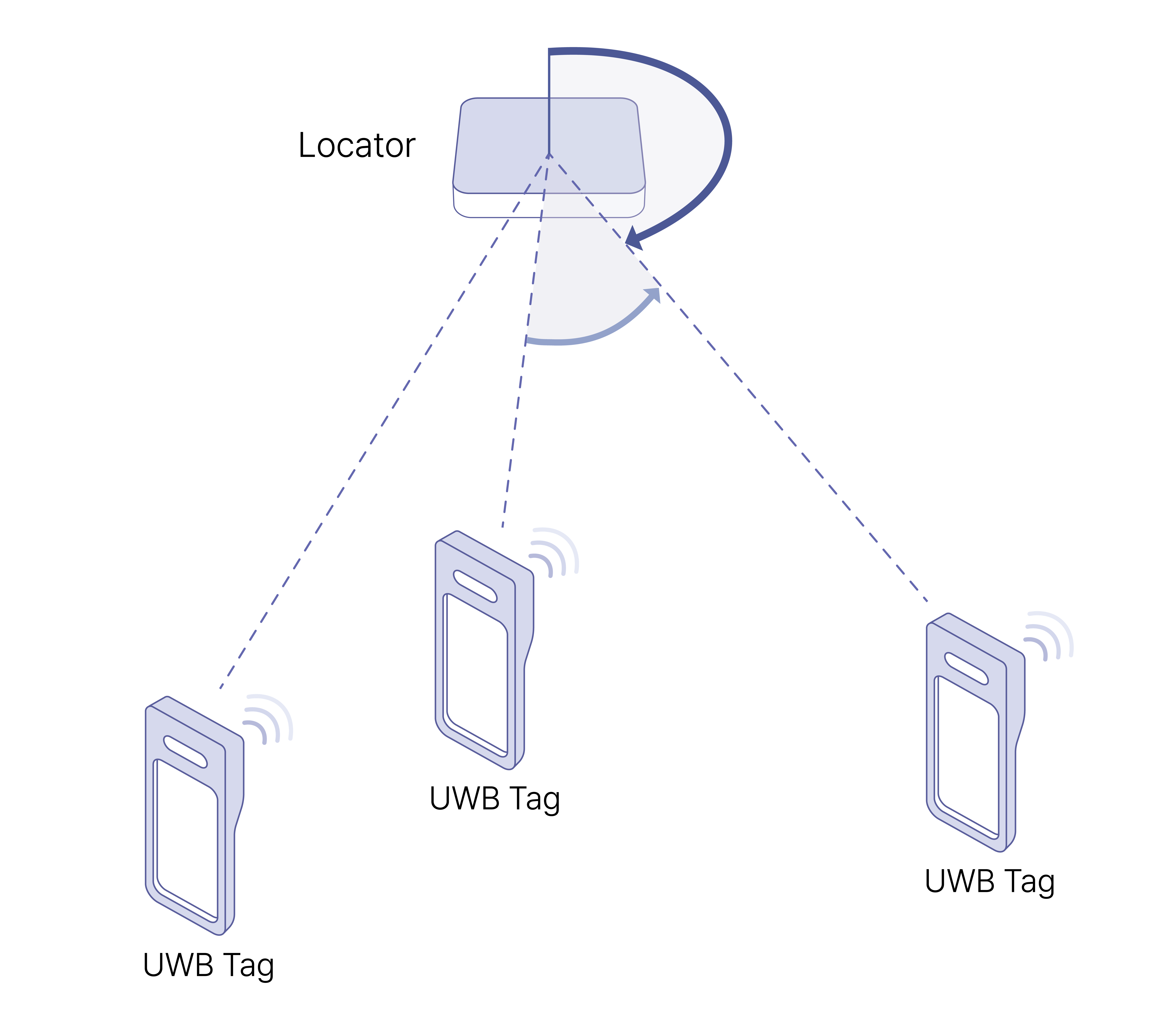
AoA positioning calculates the angle of UWB signals arriving by using the time difference (Phase Difference) arriving at each antenna based on the UWB array antenna in a device, and by substituting the vector value with the position and angle of the locator, the position of the UWB device is identified. Compared to TDoA, positioning can be calculated using less infrastructure.
BLE is a technology adopted starting with Bluetooth 4.0, and it is a wireless communication technology that started from Wibree, an in-house project of Nokia, until it was developed by the Bluetooth standardization group, Bluetooth SIG.
The biggest differentiator of BLE is that it communicates using much less power than the older Bluetooth classic. In terms of numbers, it's about one tenth. At this level, even a small cell battery can communicate for more than a year. This dramatic change in power consumption made a huge impact on the Bluetooth market. Most of today's wearable devices or IoT sensors utilize BLE wireless communication, which created a huge ecosystem and has been used in indoor positioning technology.
When BLE is used in positioning technology, it finds the position of the device via RSSI. Because this RSSI provides position using the strength level of that signal, whether the device is transmitting a strong or weak signal relative to the sensor, it has a much shorter range and data rate than UWB, is more susceptible to signal interference, and has the relative disadvantage of being vulnerable to security.
A common approach to estimating distance or position from a Wi-Fi signal is to measure the signal strength, similar to Bluetooth. Signal strength is the Wi-Fi data most readily available to smartphones and mobile devices. However, estimating distance from signal strength presents the same problems described for Bluetooth.
Some companies developed alternative algorithms that attempt to accurately measure distance using the time-of-flight (ToF) or time-of-arrival (ToA) of Wi-Fi signals, but Wi-Fi indoor positioning using standard Wi-Fi is not possible with existing infrastructure. Alternatively, it is easy in that it uses the existing infrastructure by using a custom-installed sensor, but like BLE, the error range of location accuracy is 5-15M, which is very low in position accuracy.
UWB is the abbreviation of Ultra Wide Band, which means ultra-wideband short-range wireless communication technology. UWB is a next-generation wireless technology that uses a very wide frequency bandwidth and is applied to communications and radar. UWB transmitters send out billions of radio signals across a wide spectrum of frequencies, and UWB receivers convert those signals into data. A UWB signal is used to detect the distance between two transmitters, and the shorter the duration of this signal, the more accurate the distance measurement becomes. UWB transmits up to 1 billion signals per second (1 per nanosecond), enabling real-time accuracy. In addition, UWB uses very low power and has a high bandwidth, which are advantageous for transmitting a lot of data from a transmitter to another device.
UWB is still a new technology, and companies working on it are just getting started. The FiRa Consortium, consisting of global companies, such as Samsung and Apple, is focused on advancing UWB standards and certification program updates to promote UWB technology adoption and ensure interoperability. UWB with precise positioning has advantages over BLE and Wi-Fi in terms of both precision and security, and thanks to such characteristics, various UWB applications are being developed. By providing real-time position-aware information and precise analytics, new UWB services will emerge for consumers and businesses. Representative applications include hands-free access control, position-based services and device-to-device applications as shown below.
UWB-based positioning technology provides a high level of positioning precision.
UWB positioning precision makes previously impossible applications a reality.
UWB positioning technology is effective for customers who need a high level of position accuracy.
Geoplan's RTLS technology plays a critical role in providing accurate position and data of the target.
Companies that incorporated RTLS can increase work efficiency, improve productivity and reduce losses,
while responding quickly to market changes. As the demand for indoor positioning increases
in the market and as technology advances, UWB communication will be developed into a higher level technology.